Easy Woodworking Projects
Cutting Boards
Safety Tips
- Safety glasses or goggles should be worn whenever power
tools are in use and when chiseling, sanding, scraping or hammering overhead.
This is very important for anyone wearing contact lenses.
- Wear ear protectors when using noisy power tools. Some
tools operate at noise levels that damage hearing.
- Be careful of loose hair and clothing so that it does
not get caught in tools; roll your sleeves up and remove jewelry.
- The proper respirator or face mask should be worn when
sanding, sawing or using substances with toxic fumes.
- Keep blades sharp. A dull blade requires excessive
force and can slip which causes accidents.
- Always use the right tool for the job.
- Repair or discard tools with cracks in the wooden
handles or chips in the metal parts.
- Don't drill, shape or saw anything that isn't firmly
secured.
- Oily rags are spontaneously combustible, so take care
when you store and discard them.
- Don't abuse your tools.
- Keep a First Aid Kit on hand.
- Do not work with tools when you are tired. That's when
most accidents occur.
- Read the owner's manual for all tools and understand
their proper usage.
- Keep tools out of the reach of small children.
- Unplug all power tools when changing settings or parts.
KNOW WHERE YOUR HANDS ARE AT ALL TIMES!
Most Common
Mistakes
The single most common mistake in any do it yourself
project is the failure to read and follow the manufacturer's instructions for
any tool or material being used. Other common mistakes include taking the safety
measures that are laid out for a project for granted, and poor project planning.
Here is a list of hints to successfully complete this project and to do it
safely.
- Follow the "Golden Rule" of measuring: "Measure twice,
cut once."
- Provide yourself plenty of time for each step.
- Understand your plan. (if you have questions, review
that part of the videotape).
- When finishing the wood, keep dust and dirt away from
the table.
- Follow the application instructions for your choice of
finish.
- Allow an extra ¼" to " inch when cutting the stock.
- Experiment with scrap wood before you work on the real
piece. This will help with finishing touches.
Project Introduction
Terminology
Before you begin your project, you will want to become
familiar with the woodworking terms shown below.
- Miter Cut - Angle cut across the width or
thickness of the board
- Rabbet - L-shaped cut
- Dado - Channel cut across the board, into which
a second piece of wood is fined
- Kerf - Width of the blade
- Countersink - To set a screw head at or below
the surface
- Dowel - Wooden pin used to provide strength and
alignment
- Chamfer - Corner of a board beveled at a 45
degree angle
- Laminate - Composed of firmly united layers of
wood.
Materials
Wood Selection
The two basic categories of wood used most often in wood
working projects are hardwood and softwood. Hardwood is more durable and less
prone to dents and scratches. It is also more expensive but will finish to a
better advantage. Soft woods, like pine, are more prone to dents and scratches
and do not have the durability of hardwood. Softwoods are much less expensive
and easier to find.
Ask your lumber supplier to show you "Class 1 " or "Select
Grade" lumber. Make sure it is properly dried, straight, and free of knots and
defects. (It may be impossible to be completely free of defects but be sure you
understand how to cut around these.)
Ask your Lumber supplier for assistance when purchasing
your wood. Similar to laying a pattern out on a piece of cloth, often you can
cut several different pieces of the same thickness of wood out of a single
piece. It is a good idea to add up the total number of board feet, being careful
to make sure you group short pieces in a board with long pieces to minimize
waste.
This project could be built out of scrap wood already in
your workshop. If you choose to use new stock from the lumber yard, both
hardwoods and softwood are good choices.
Note: Developing a good relationship with Your
lumber suppliers is important. They can help guide you in making material
selections as well as making special orders for a type of wood you may desire
for a project.
Now that you have reviewed safety hints, learned the
mistakes to avoid, reviewed the basic components and gathered your tools and
materials for your projects - you are ready to BEGIN!
These are the steps to
follow for the cutting board:
- Cut the stock
- Laminate the boards
- Finish the board
Cut the Stock
- The block thickness is determined by the width you cut
the individual pieces. Example: For a block to be 111 thick you will cut the
stock 1" wide because of the lamination process which will group the boards
together.
- Cut the stock a little longer than you wish the length
of the cutting board to be. You will cut the board to the finished side after
it has been laminated and sanded.
Laminating the
Stock
- Use resorcinol glue on both sides of the stock to glue
them together. Resorcinol glue is water proof and will provide stability if
the board is soaked in water.
- After gluing, clamp the boards together and let dry
overnight.
- Scrub off extra glue before it dries to prevent
chipping the cuffing blades when finishing and shaping.
Finishing the
Cutting Board
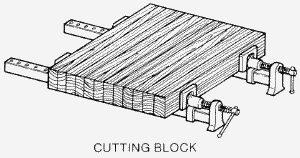
- After the board dries, take out of the clamps and use a
belt sander to smooth the top and bottom surfaces.
- Using a table saw or circular saw, cut the board to
length. If using a table saw be sure that the cutting blade does not exceed
1/4" above the cutting board to prevent drag.
- Using a shaper or router put around over edge on the
top surface of the cutting board. Be careful to follow the guidelines reviewed
in the tape.
- Use a non-toxic finish such as mineral oil or a salad
bowl finish for this project
